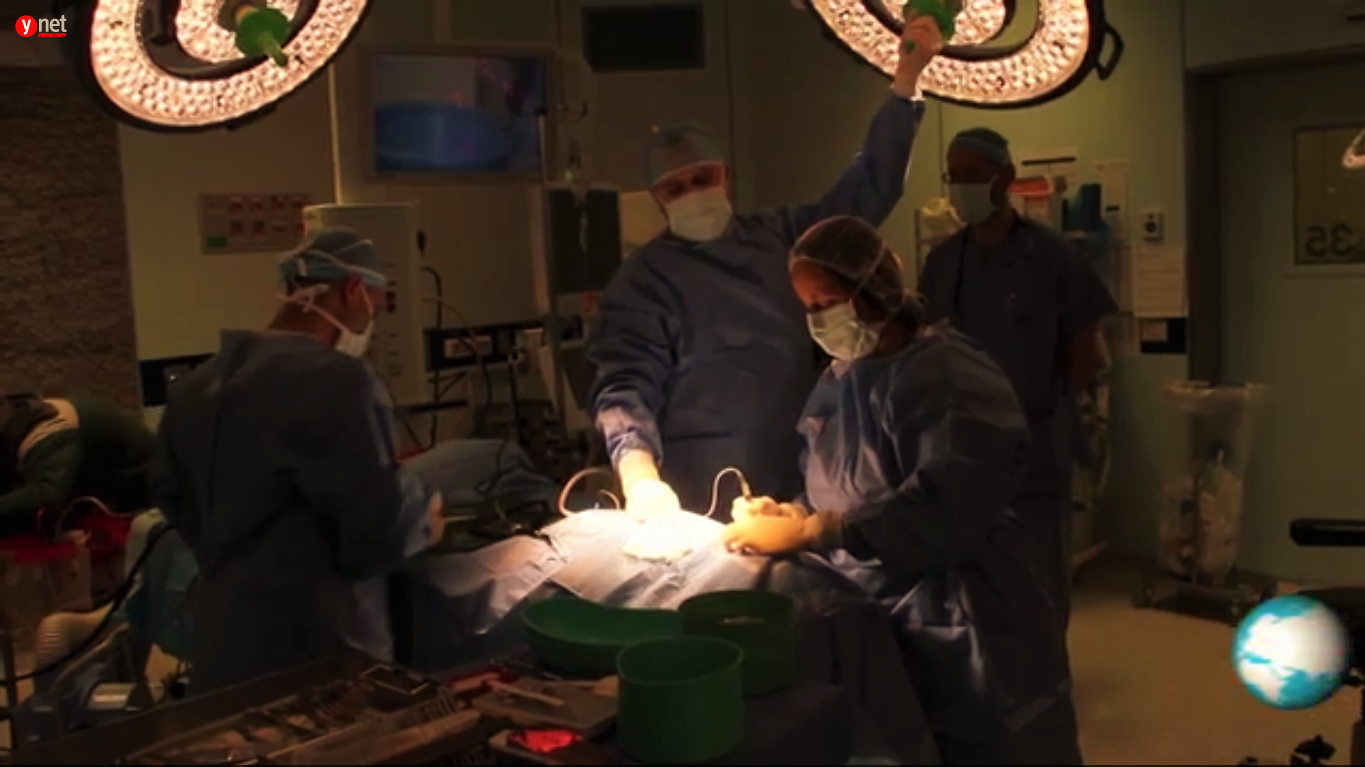
Нейрохирургические операции у детей в Хадассе
КЛИНИКА ХАДАССА ПРИНИМАЕТ ПАЦИЕНТОВ.
МЫ ПОМОЖЕМ В ОРГАНИЗАЦИИ:
- удаленных - дистанционных консультаций
- получения второго мнения
- лечения в израильской клинике (после рассмотрения документов в индивидуальном порядке)
- лечения в клиниках ОАЭ и Кипра
Узнать больше
В департаменте детской нейрохирургии проводят все виды операций на головном или спинном мозге, успешно вылечивая следующие заболевания:
- опухоли мозга
- гидроцефалию
- краниосиностоз / нарушения строения черепа
- врожденные дефекты ЦНС
- врожденные дефекты сосудов головного мозга
- эпилепсию
И другие патологии.
Диагностика и лечение в департаменте выполняется многопрофильной командой ведущих израильских специалистов: неврологов, онкологов, радиологов, экспертов по интенсивной терапии, физиотерапевтов, социальных работников, реабилитологов и многих других.
Fields of Treatment:
Pediatric Brain Tumors
Among the tumors we see in children, brain and spinal cord tumors are second in prevalence after blood cancers. These tumors may be completely benign or very malignant, but usually the symptomatology is similar.
A brain tumor can appear in any brain region, but in children it most often develops in the cerebellum, which is located in an indentation at the back of the skull. The tumor may cause an increase of pressure inside the cranium and characteristic symptoms and signs that result from higher pressure, especially headaches accompanied by vomiting, sleepiness and new strabismus.
In babies, one can note irritability, reduced appetite, receded development, a bulge in the fontanelles and so on. It can also cause weakness in a part of the body, postural and walking difficulties, speech and swallowing difficulties, hoarseness and more.
A child with a brain or spinal cord tumor usually arrives at the pediatric neurosurgery unit after the diagnosis has already been made by the primary physician in the community or the hospital emergency room. When the child arrives in the unit, the multidisciplinary team performs a continued diagnosis and treatment.
Such a child needs to undergo an MRI scan of the brain and often of the spinal cord; after that, decisions are taken on the need for surgery and how urgent it is. Often, an urgent operation is required to lower the increased intra-cranial pressure that such children suffer from.
A week after surgery, the final diagnosis is obtained, and continued treatment (if at all) is decided upon in accordance with the type of tumor. Then follow up alone may be needed or also chemotherapy, radiation and perhaps a second operation.
There is no doubt that for the parents and the wider family, the bitter news of a tumor in the child’s brain constitutes a major earthquake. But at the same time, it should be noted that the abilities of modern microsurgery — including the use of a GPS-based navigation system and ultrasound imaging during the operation, together with support from the pediatric intensive care unit after surgery and supportive treatment from oncologists — has brought about significant improvement in those children’s prognosis.
MRI scan of a 10 months old child with a brain tumor
Hydrocephalus
In the brain there are areas or spaces that contain water like fluid that is called cerbro spinal fluid (CSF). Hydrocephalus is defined as an increase in the volume of the CSF in the ventricles of the brain that causes a rise in intracranial pressure. The CSF is being produced constantly, flows between the different ventricles and being reabsorbed to the blood stream. The CSF may accumulate in the ventricular system when there is a problem in the reabsorption to the blood. This can often be seen in premature babies who suffered from intraventricular hemorrhage, meningitis or other similar conditions. In this type of hydrocephalus all the ventricles are connected between them and they are all enlarged. Hence, this condition is called «communicating hydrocephalus».
Hydrocephalus can also results from a physical blockage in the passage of the liquid between the various ventricles. Since the flow of the fluid is obstructed, there is no communication between the ventricles, this is called «obstructive hydrocephalus».
The accumulated fluid causes an increase in intraventricular pressure and the clinical symptomatology characterized by this increase in pressure, as described here. Treatment is surgical, as there is no other way to reduce this pressure except to create alternate ways for it to be drained. The most common surgery for «communicating hydrocephalus» is by inserting a vntriculo-peritoneal (V-P) shunt, which since it was introduced it dramatically changed the prognosis for these children.
In the past, this was also the method of choice for treating obstructive hydrocephalus. But today, an intra-ventricular endoscope can be inserted and microsurgery used to perform endoscopic third ventriculostomy- which is a small orifice in the floor of the third ventricle, to create a kind of bypass of the blocked region so the fluid can drain directly into the subarachnoid space; from there, it flows back to the circulating blood. This operation is effective in 75 percent of cases and eliminates the need to insert a shunt, which is actually a foreign body.
CT scan of a child with a «communicating hydrocephalus»
Craniosynostosis
At birth, the skull is comprised of a large number of bones that, as the child grows, join together. These bones are connected between them in sutures that allows the cranium (and the brain) to grow. Sometimes there is a premature closing of one or more sutures, reforcing the brain and the skull to grow in an asymmetrical pattern. This irregular skull growth is not esthetic and in the long term can cause cognitive problems and attention deficits in these children.
Surgical repair of an asymmetrical skull has been carried out at the age of several months in cooperation among neurosurgeons and plastic surgeons. This is aimed at producing the optimal cosmetic and functional results. The integrated team also operates on children with Crouzon’s, Pfeiffer’s and Apert’s syndromes.
Congenital defects
The department has a lot of experience in diagnosing and treating opened and closed defects of the central nervous system. Often, these defects are diagnosed clearly before birth, and the family receives prenatal consultation accordingly.
In such deformations, there is usually no complete fusion of the neural tube and often one can see parts of the brain and spinal cord bulging outside the body. Preventive care for these defects includes the woman taking folic acid supplements before she gets pregnant. Treatment for the babies includes surgery to close the defect and the intervention of a multidisciplinary team that can significantly improve the children’s quality of life.
Head trauma
In most children who die from physical trauma, brain damage is the cause of death. Treatment for serious and moderate head trauma is complex and often requires urgent surgical intervention. The situation must be monitored constantly, followed by a long process of rehabilitation.
The department works in close collaboration with the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. This collaboration saved many lives of children with severe head trauma.
Although sometimes we witness real successes in such children, there is no doubt that the best treatment of head trauma is prevention, by wearing a protective helmet while riding a bicycle, skateboard, skates and the like; seatbelts in vehicles; and suitable railings in buildings. The effort to prevent such injuries is tiny compared to the anguish and suffering of the child and the family as a result of head trauma.
Arterio-venous malformations and other vascular anomalies
The department has great experience when it comes to the management of children with AVM. Together with the endovascular, skull base and vascular surgeions team we can offer the best diagnostic and surgical facilities to these children. Patients who suffer from other vascular defects such as Moya Moya, A-V fistula, etc, can also benefit from the abilities of this team.
Epilepsy Surgery
The multidisciplinary center for epilepsy is now being established at Hadassah medical center. This center will provide optimal treatment for children and adults who suffer from epilepsy especially those who have drug resistant epilepsy. These patients sometimes experience dozens seizures everyday, and for some of them we can offer cure of their disease.
Please contact Dr. Benifla, Director, The Department of Pediatric Neurosurgery, for any question or consultation:
+972 505 172 174
Benifla@hadassah.org.il
The Department of Pediatric Neurosurgery is located on the ground floor at The Mother and Child Center, Hadassah Ein Kerem.
For appointments, please call +972 2 584 2111
For private medical treatment, please call + 972 2 677 8899
 Россия:
Россия: Украина:
Украина: Израиль:
Израиль: